STATIC AND DYNAMIC ELECTRICITY for Class VII
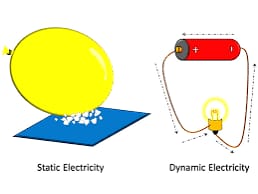
Static: Static electricity is the result of an accumulation of electric charges that occurs when two non-metallic objects rub against each other: for example, when we rub a balloon and it sticks to the wall. Electrons jump from one object to the other, causing a positive charge in one and a negative charge in the other.
Dynamic: Dynamic electricity is the flow of electric charges through a conductor; in other words, an electric current.
Comments
Post a Comment